Physical Architecture
System Database
·
Distribution database
·
Master Database
·
Model Database
·
MSDB
·
Temp Database
·
Resource Database
File group is the logical container. Using the file
group you can describe the MDF file what type of database creation. This is the
new feature from the SQL server 2008 R2.
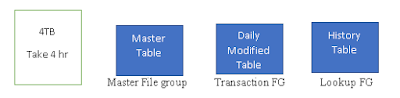
You can take back up of the database depending on the
file group. Suppose an organization has database of 4TB that they need to take
back up at that time while creating the databases they need to device the mdf
file in particular file group. If that database taking 4 hr of time to complete
backup we can take file-group back up to reduce the time lag.
As showing in above figure, we
can divide the databases in FG ( File Group) and take backup of only Transaction FG to reduce
the time and space of backup.
The first file that you create
while creating database is extension with .mdf
for data and .ldf for log file.
However the second data file that you create will have extension as .ndf .
The main database that has
created it should be File type of RAW
DATA
Database size should be in MB So you can know exactly how much space will get utilize and
needed.
There is only one .mdf file which always belong to primary file group. In .ldf logical files data is being
written in sequentially format. If there is two logical files then second one
is being used after 1st one is full.
Syntax to define file group
using the query window.
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[Test](
[id] [int] NULL
) ON [PRIMARY] Here Primary
is file group.
GO
PAGES
In the database mdf data first store in pages. Where
page is basic storage unit.
One page size is equal to 8kb = 8196byte.
Each page divided into three catogeory
1. Header – 92bytes It store page
number, page type, amount of free space it has, allocation unit ID of the
object that owns the page.
2. Data Row -8096bytes it contain actual
data. Data is being stored one after another. At the end of the page a row offset table exist which store one
row for each data row in pages.
3. Footer -8bytes it contain information
as which one is the next page and which once was previous page.
There are 9 types of pages in SQL server.
1. Data It contain Data rows with all
data expect text, ntext, images, nvarchar (max), varchar (max), varbiary (max)
and xml data, when text in row set to ON.
2. Index - Index entries
3. Text/Images – Large
data and text, images, ntext data.
4. Gam – Global Allocation Map.
Information about allocated Extents. Store only uniform extend information.
Like free space at what location is available.
5. SGAM – Shared Global Allocation
Map. Contain information about mixed extents.
6. PFS – Page Free Space. This is the
first page of every database file. It contain the available free space
information. It also contain the page allocation.
7. IAM- Index Allocation Map.
Information about extends used by the tables or index per allocation unit.
8. BCM- Bulk Change Map. Contain the
information about extends modified by bulk operations since the last backup LOG
statement per allocation unit.
9. DCM- Differential Changed Map.
Information about extents that have changed since the last backup database
statement.
EXTENTS
An
extents is 8 continues pages or 64kB memory space.
There
are two type of extents
1. Uniform Extent – All 8
pages in the extent are owned and used by a single object.
2. Mixed Extents – Each of
the 8 pages in the extents may be owned and used by different objects.
A new table or index is generally allocated pages from
mixed extents. When the table or index grows to the point that it has eight
pages, it then switches to use uniform extents for subsequent allocation.
64000 Extents are cover by a single GAM/SGAM.
To allocate a uniform extent, the DB engine searches
the GAM && to allocate a mixed extent, it search in the SGAM.


No comments:
Post a Comment